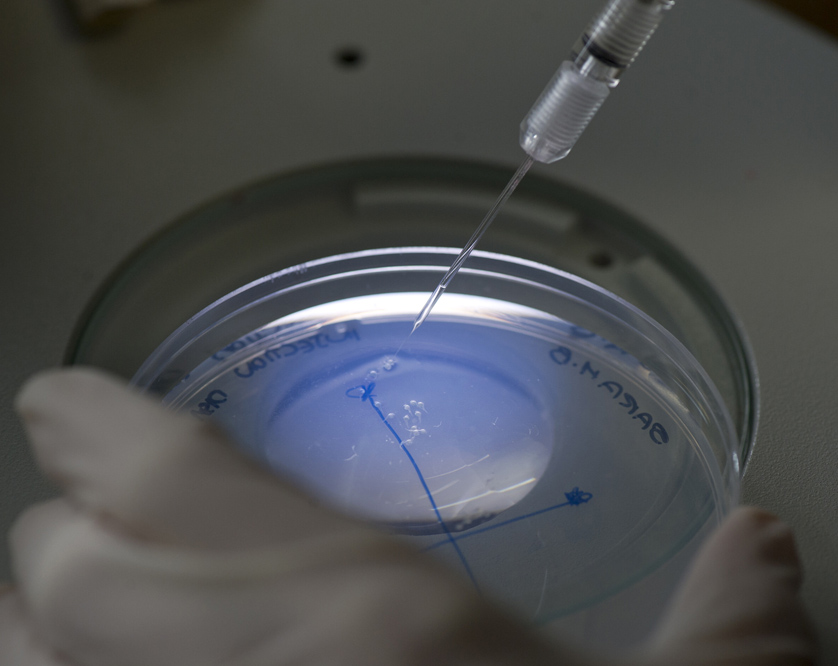
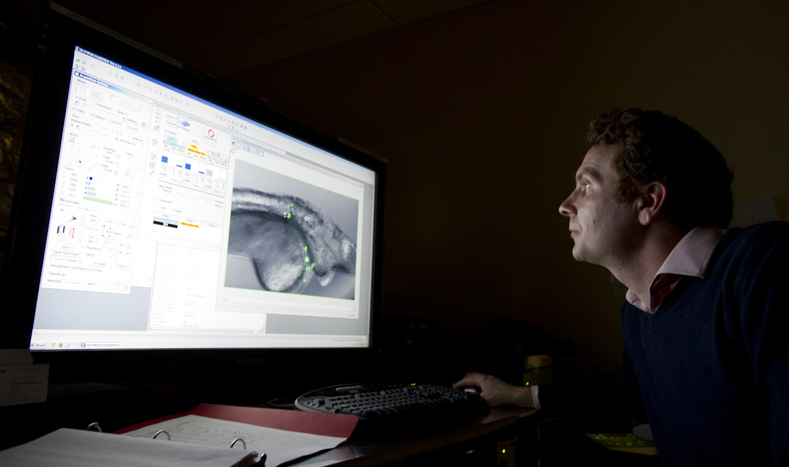
Contaminant effects on Maine finfish
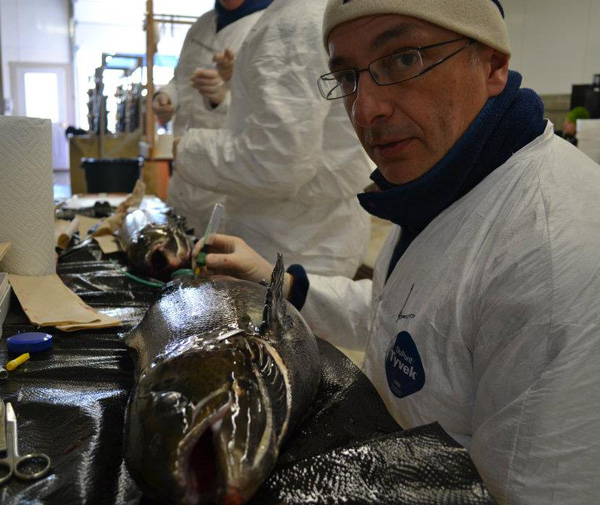
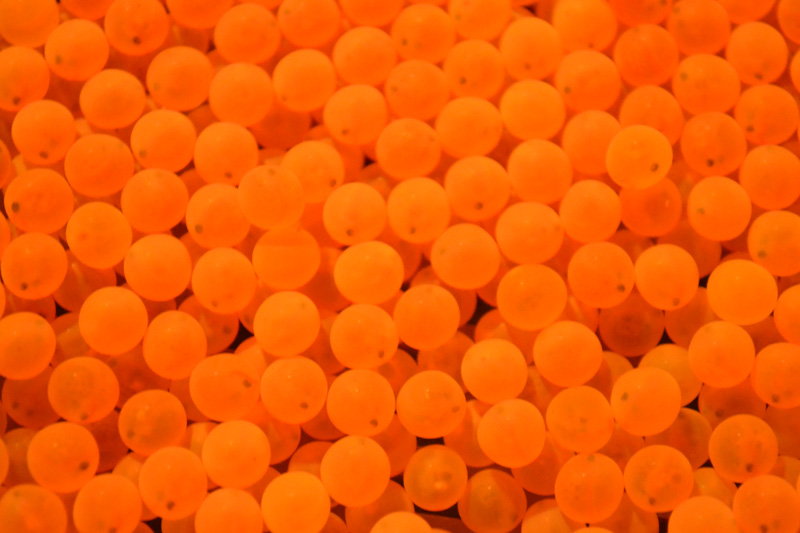
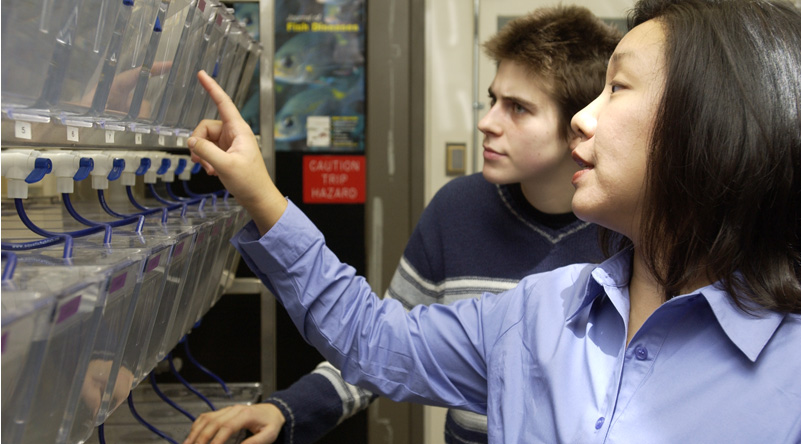
Arsenic contamination of watersheds is particularly problematic in Maine with its high levels of arsenic in underlying bedrock that contaminate groundwater at levels that often exceed EPA allowable safe limits (10 ppb). Relatively little, however, is known about the effects of arsenic at these low levels of exposure. Fish may be particularly vulnerable as they […]
Read more