Models and Data
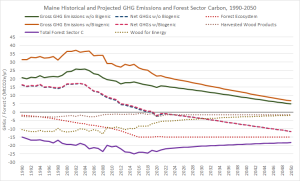
Maine Greenhouse (GHG) Emissions and Forest Sector Carbon Sequestration, 1990-2050
Maine’s historical (1990-2021) and projected (2022-2050) greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and forest sector carbon sequestration. GHG emissions include fossil, agricultural, and biogenic (including biomass) sources. Forest sector carbon sequestration includes forest ecosystem and harvested wood products.
Data and sources available for download in this Excel Spreadsheet.
A Resilience Indicators Approach to Ensuring Equitable, Objective, and Continued Investment in Northern Border Communities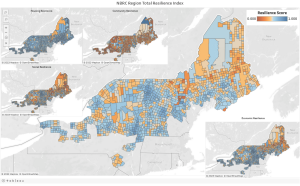
This collaborative research project was undertaken to better understand community resilience in the Northern Border region, a federally designated area of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York that borders Canada and generally has higher levels of unemployment, population loss, and lower incomes than neighboring areas. The long-term goal of this work is to develop objective metrics that can help align strategic federal and state investments in this region.
A key output was to develop a set of quantitative indicators of socioeconomic resilience for Northern Border communities. These indicators can be accessed and visualized through this Tableau Dashboard.
Full project report available here.
Forest Carbon for Commercial Landowners (FCCL) Project
The FCCL project was designed to evaluate whether commercial forest landowners in Maine could increase carbon sequestration in the forest and in harvested wood products by employing various silvicultural practices that would cost-effectively mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
Project report available here.
Modeled silvicultural practices and forest types available here.
FCCL model estimates available for download in this Excel spreadsheet and presented in Tableau.
Maine Mill Database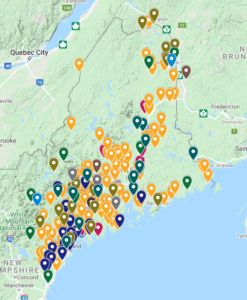
Compilation of different open and closed forest product companies across and close to Maine (where they may use Maine timber supply), including mills, biothermal plants, secondary sellers, and other forest products industries. Production numbers were gathered from various databases and direct contacts with business owners.
Data was compiled in a google spreadsheet but can also be viewed in google maps.
.
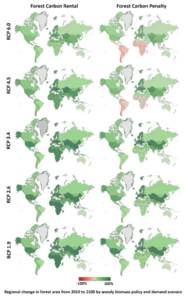
Global Timber Model (GTM)
Global forests are subject to a wide range of socioeconomic, policy, and natural pressures. The potential impact of these pressures on forest area, harvests, timber markets, and carbon stocks, can be analyzed using the Global Timber Model (GTM). GTM is an economic model capable of examining global forestry land-use, management, and trade responses to policies across more than 300 unique forest ecosystems. The model estimates timber harvests in managed and inaccessible forests, timberland management intensity, and plantation establishment, all important components of both future timber supply and carbon flux. GTM has recently been used to evaluate impacts associated with bioenergy policy, shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs), and forest tax policy.