Maine’s Glacial History Vocabulary
Post-glacial rebound
The weight of a glacier is so great that the continent sinks beneath it. As glaciers melt, the continent rises back up out of the magma or “rebounds” like a rubber duck pushed down into a bathtub full of water.
Tundra
An arctic and sub-arctic biome or zone where trees will not grow. The vegetation consists of low growing plants such as mosses, lichens, and shrubs.
Pleistocene
A geological epoch that began 2.6 million years ago and ended around 12,000 years ago at the beginning of the Holocene—the epoch in which we live. The Pleistocene was characterized by the end of the last glacial period and is the period of time during which present-day humans evolved and spread throughout the planet.
Resources
A term used to cover all the things a group of people need for daily life, including items necessary for food, shelter, clothing, and tools.
Artifact
Anything used or modified by people.
Archaeological periods
Lengths of time during which the kinds of artifacts found in a given area tend to be of similar styles and purposes, including those found in different kinds of sites (habitation sites, camps, workshops, mortuary sites).
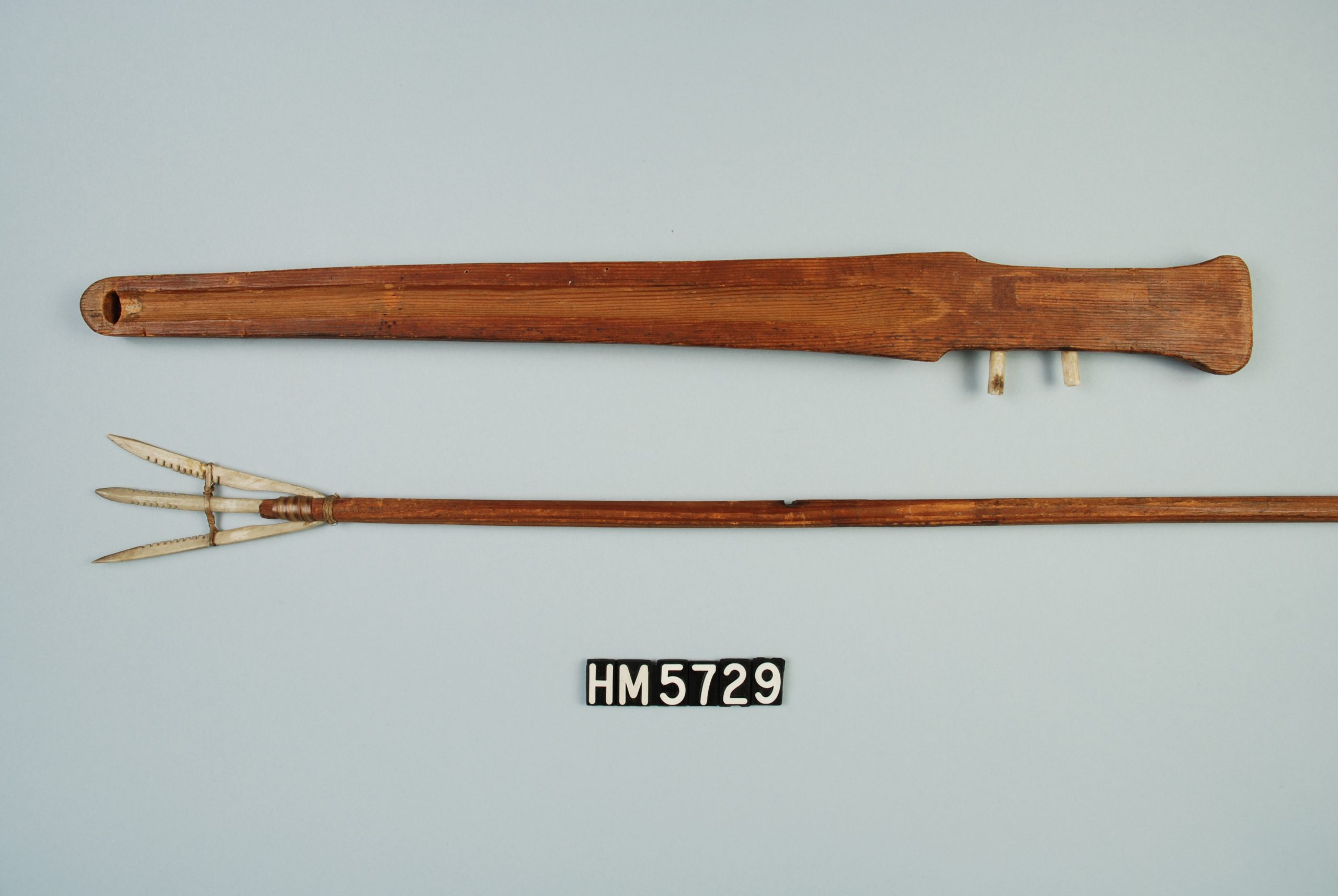
Projectile point
A pointed artifact attached to the tip of a projectile such as a spear, a dart, or an arrow. These are often made from stone through a chipping process called “knapping”, however they can also be made of bone or wood or by alternative methods such as grinding.
Atlatl
A tool used to throw a dart or spear farther and harder than could be thrown by hand.

Ground stone
A method of making stone tools that includes first creating a general shape through flaking or pecking and finishing the object by grinding it into a final form.
Celt
A tool with a beveled edge, generally ground from stone, and presumably used for woodworking.

Adz
A tool much like an ax, but with the blade hafted at a right angle to the handle. Used to shape large pieces of wood.
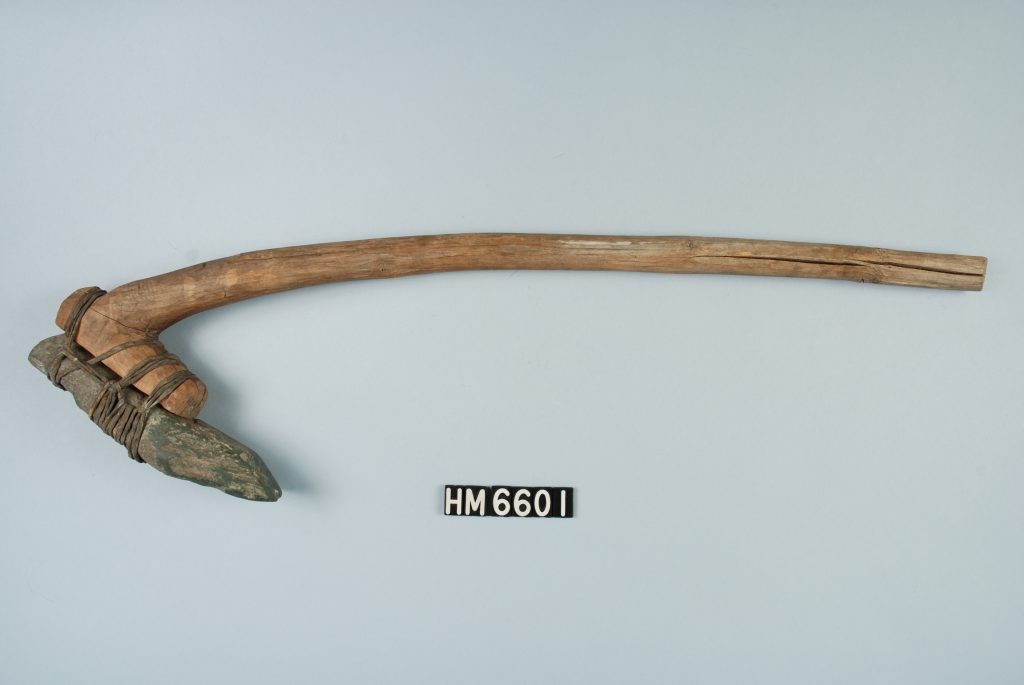

Gouge
A tool with a grooved channel used to carve wood.

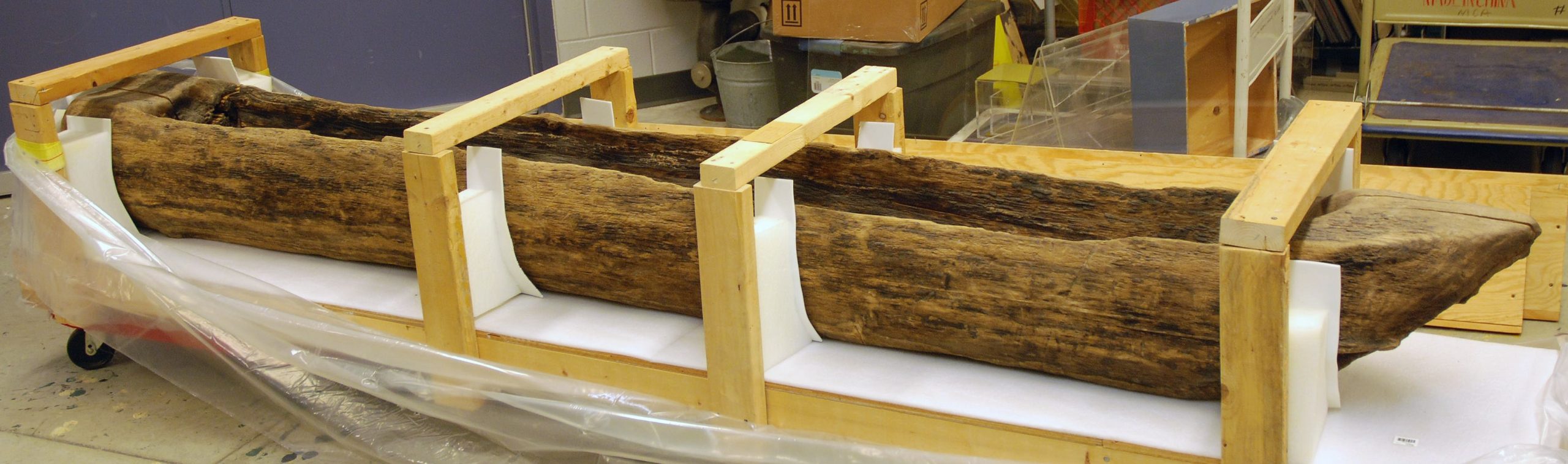
Dugout canoe
A canoe made by hollowing out a log.

Plummet
A ground stone object made with a groove for attaching it to a string or cord, presumably used as a weight, possibly for fishing with a net.

Archaeological tradition
A collection of artifacts frequently found together in similar kinds of archaeological sites.
Material culture
All of the physical things (tools, clothing, housing, jewelry, etc.) used by people in a given time and place.
Aquatic
Having to do with the water.
Terrestrial
Having to do with the land.
Agriculture
The planting and raising of plants for food; these plants are usually “domesticated”, meaning that they have developed different forms and requirements from their natural ancestors through human selection.
Gunflint
An important early trade item. Knapped from flint, they were used in early firearms to create a spark, which would ignite gunpowder, propelling a musket ball from the gun’s barrel.