Facilities
The Department of Energy’s only designated user facilities focused on performing early-stage research and development to improve the energy and material efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness of American manufacturers.
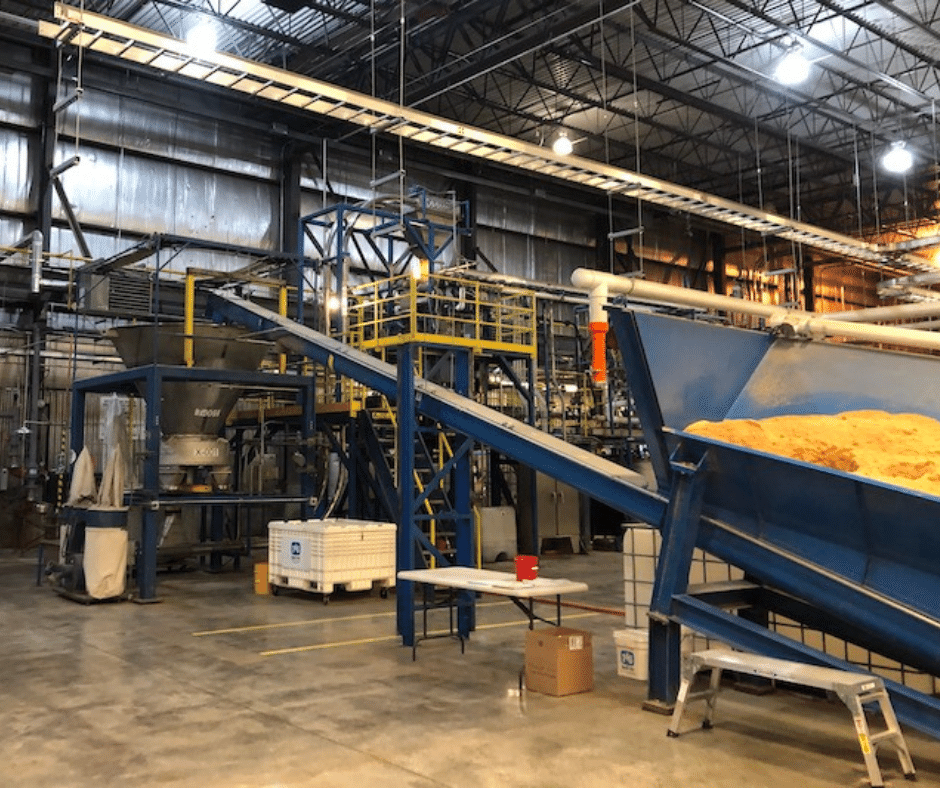
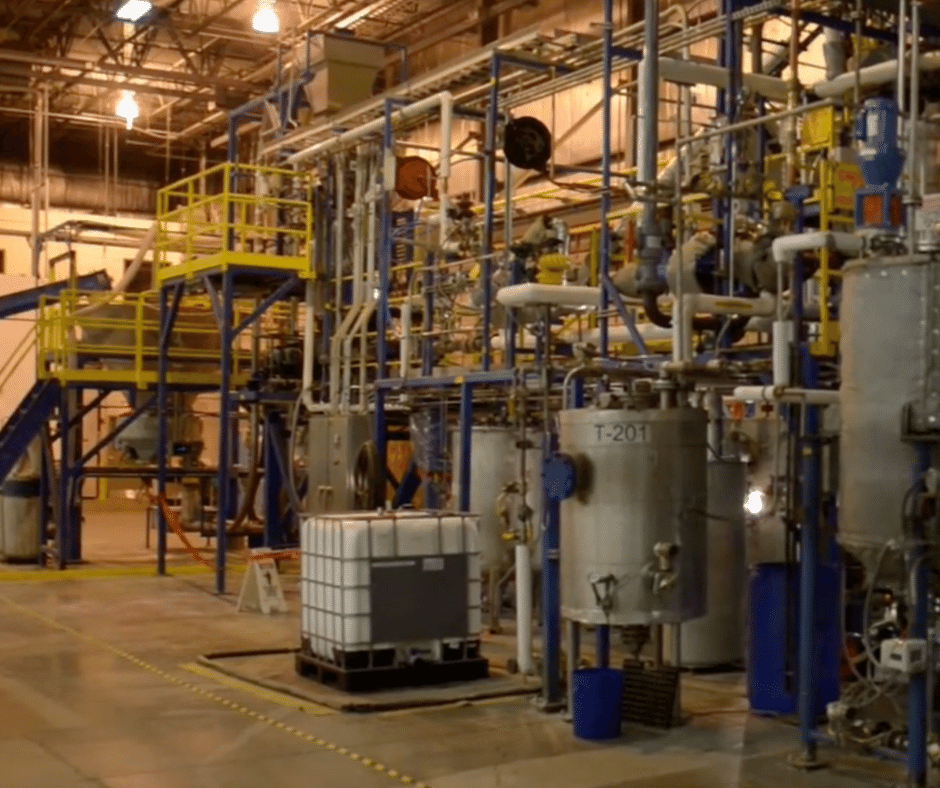
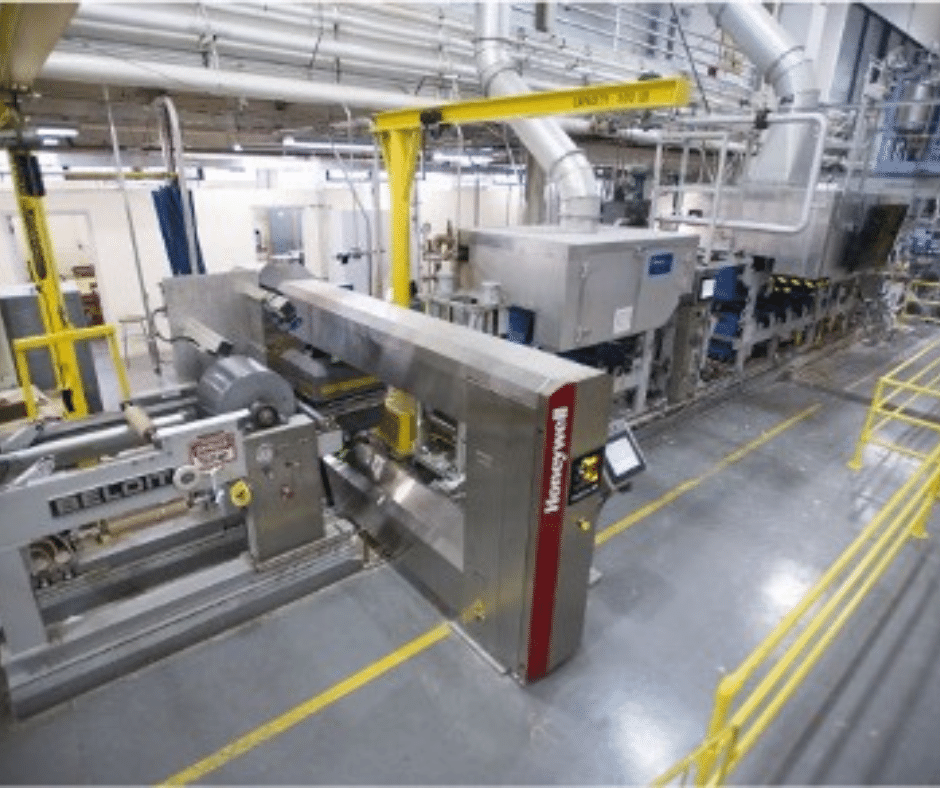
The MDF is a 110,000 sq. ft. facility housing integrated capabilities that drive the development of new materials, software, and systems for advanced manufacturing. From binder jetting to 3D tomography to in situ monitoring, the MDF leverages a range of equipment and expertise focused on reducing the carbon footprint of the manufacturing sector, efficiently utilizing abundant and available domestic energy resources, and supporting the production of clean energy products that boost the nation’s economy.
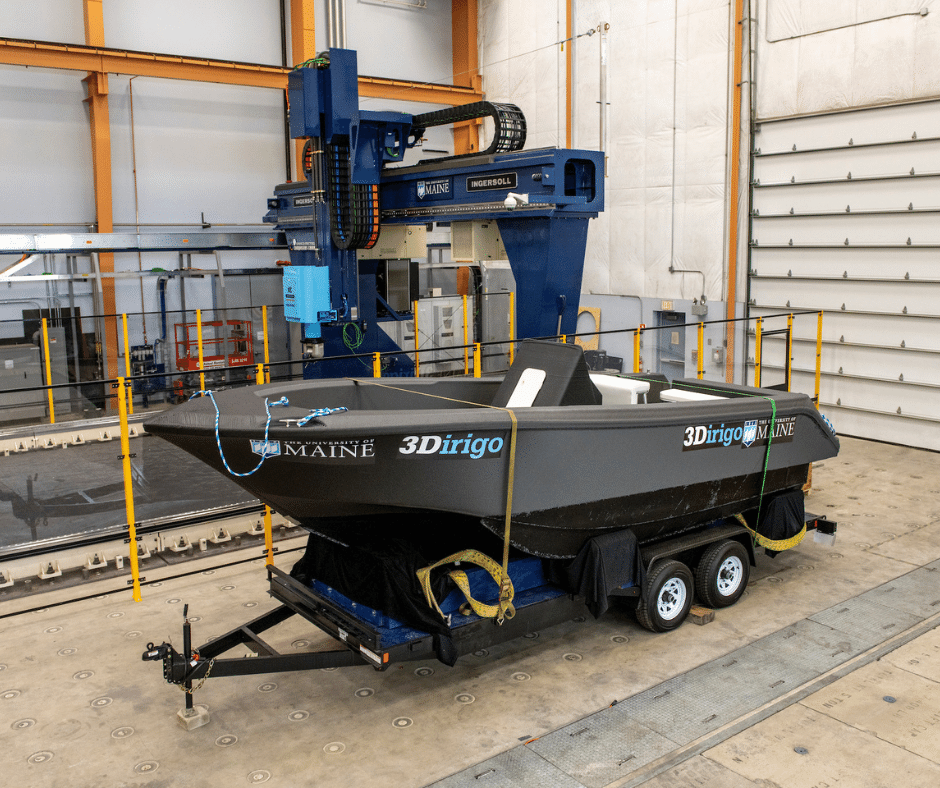
Bio-based additive manufacturing leverages bioderived, sustainable feedstocks to 3D print complex structures including products ranging from foams used in car seats and mattresses to entire boats. The process incorporates bioscience, materials science, and additive manufacturing to create biomaterials capable of delivering products with desirable qualities.
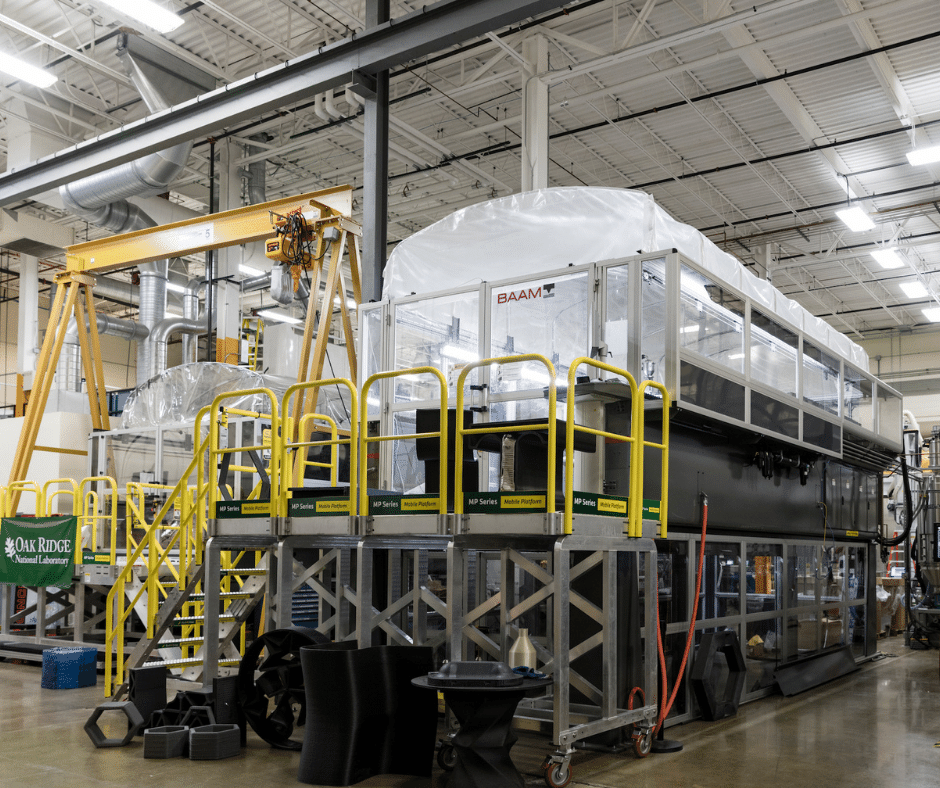


The University of Maine’s ASCC lends its expertise and innovation in forest derived biocomposites for AM purposes to the Hub & Spoke SM²ART program.
The University of Maine’s Advanced Structures and Composites Center is a world-leading, interdisciplinary center for research, education, and economic development encompassing material sciences, manufacturing, and the engineering of composites and structures. The Center is housed in a 100,000 ft2 ISO 17025-accredited testing laboratory with more than 260 full and part-time personnel.
For more than 25 years, the ASCC has been on the cutting edge of bio-based composites made with Maine wood products and is developing bio-based, renewable feedstocks using cellulose nano-fibrils for additive manufacturing.
The 2019 installation of the World’s Largest Polymer 3D printer was just one of the latest milestones the ASCC has reached as a leader in Large-Scale Additive Manufacturing. With a rich history in innovation for rapidly deployable, cost-effective, and better-made structures, additive manufacturing is the next great frontier for solving problems in any industry.
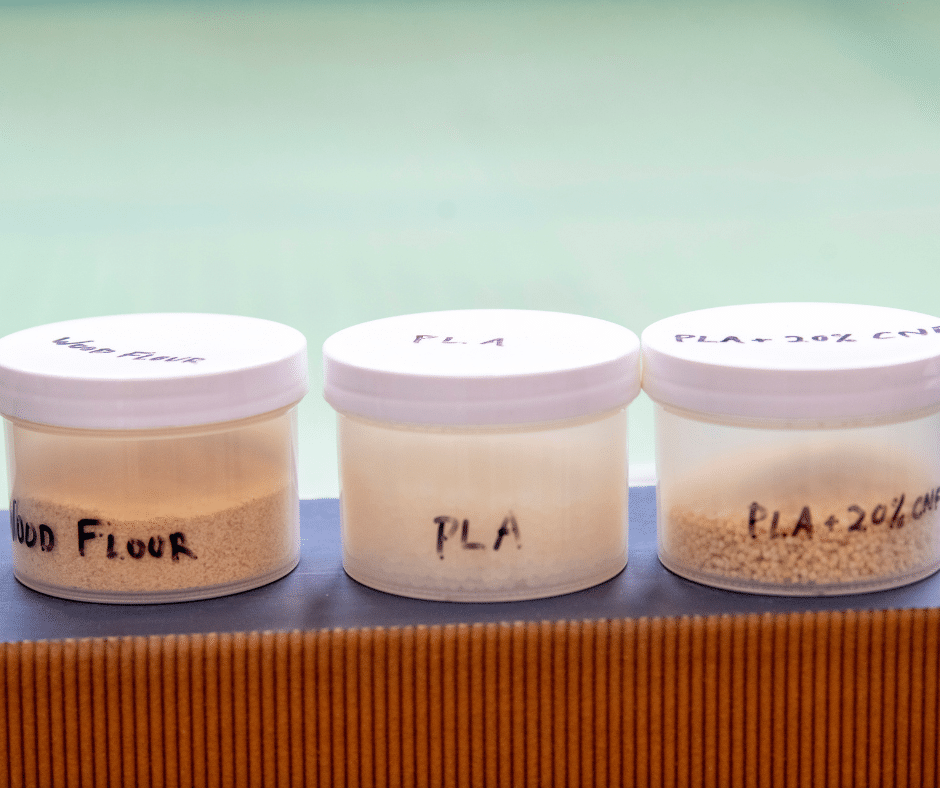
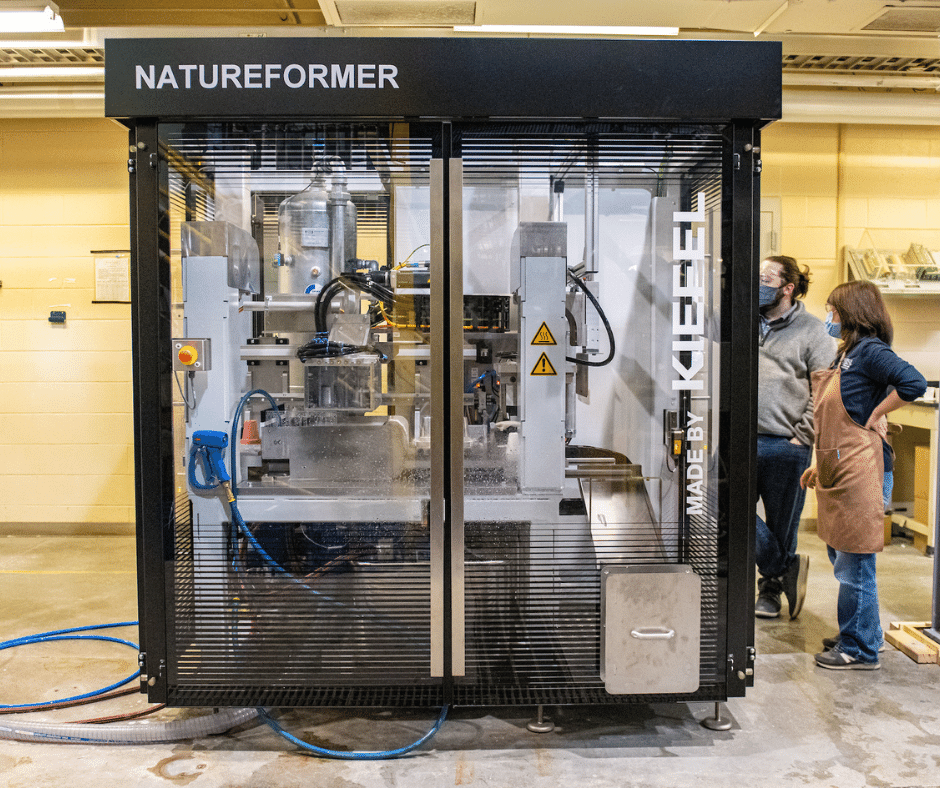
Located at the University of Maine, the PDC is the cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) provider for the Hub & Spoke SM²ART program.
The Process Development Center (PDC) at the University of Maine supplies cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) and cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) to academic, public, and private research groups interested in evaluating and developing applications for these materials. The PDC is the only facility in the United States that can manufacture cellulose nanofibers (CNF) at a rate of one ton per day. Cellulose nanomaterial varies in amount (from 0.25 pounds to metric tons) and solids content (dry, 15%, 3%). The PDC offer several types of cellulose nanomaterials:
- CNF – cellulose nanofibers
- CNC – cellulose nanocrystals
- TOCN – Tempo-oxidized cellulose nanofibers
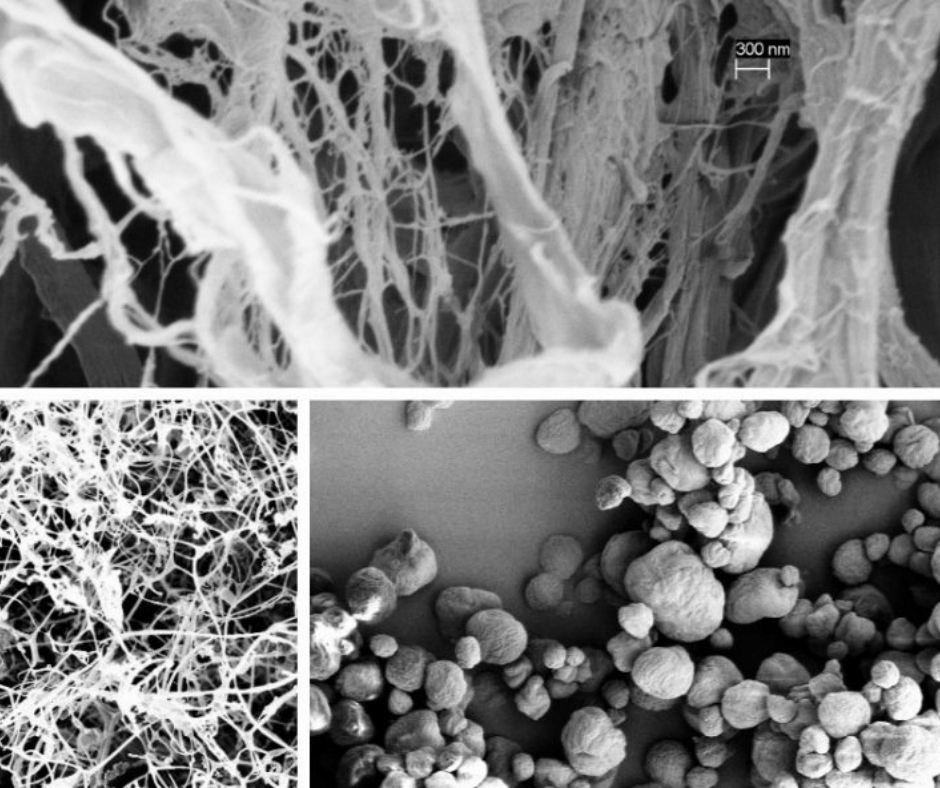
Cellulose nanocrystals are tiny, rod-like particles sourced from natural materials. Cellulose nanocrystals are derived from wood pulp and have dimensions of approximately 5 nanometers (nm) in diameter and 150-200 nanometers in length. Larger crystals can be produced using cotton (10 nm by 500 nm) or algae (20 nm by 1000nm).
Cellulose nanofibrils are noticeably longer and often branched or forked, with dimensions of 20-50 nm in width and lengths of up to several hundred microns. All of the cellulose nanomaterials produced by the UMaine PDC and by our partners at the Forest Products Laboratory are made from wood pulp. – Courtesy of PDC
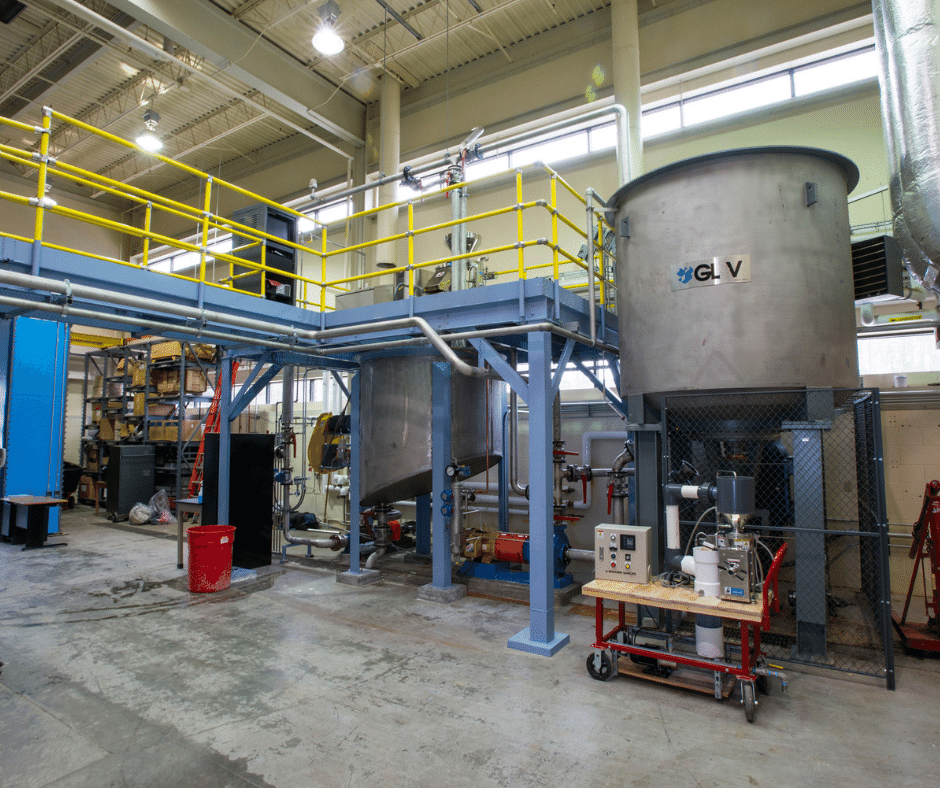

As part of the University of Maine’s Forest Bioproducts Research Institute’s, the TRC houses large scale equipment like the spray dryer and conducts chemical and advanced material technologies for processing woody biomass into feedstock
The Technology Research Center (TRC) is a 40,000-square-foot facility, located on the grounds of ND Paper in Old Town, Maine. Dedicated to validation, demonstration, and commercialization support for bioproduct development, the center is a one-stop shop for processing and analysis of technologies at an industrially relevant scale.
The reactor is a 100 L jacketed glass reactor with a squat profile that enables easier access to the ports and materials, which enables reaction volumes of up to 60 L. It is equipped with seven ports to add reactants and monitor the reaction as well as 1/4 HP agitator. Temperature can be controlled from -45 to 200 C by an external 3 kW heating power and 0.8 kW cooling power Huber Unistat circulator. Accessory glassware enables inert atmospheres and reflux as needed.